1.What is the API?
2.What is the Rest API?
3.What is the use of Web API?
4.What is ReST services?
console.log(xhr.statusTest)
8.what the four verbs?
9.Anatomy of request ?
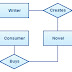
- Application program interface (API) is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for building software applications. An API specifies how software components should interact. Additionally, APIs are used when programming graphical user interface (GUI) components.
2.What is the Rest API?
- REST stands for Representational State Transfer. (It is sometimes spelled "ReST".) It relies on a stateless, client-server, cacheable communications protocol -- and in virtually all cases, the HTTP protocol is used. REST is an architecture style for designing networked applications.
3.What is the use of Web API?
- ASP.NET Web API. ASP.NET Web API is a framework that makes it easy to build HTTP services that reach a broad range of clients, including browsers and mobile devices. ASP.NET Web API is an ideal platform for building RESTful applications on the .NET Framework.
4.What is ReST services?
- RESTful Web Services: A Tutorial. ... While REST stands for Representational State Transfer, which is an architectural style for networked hypermedia applications, it is primarily used to build Web services that are lightweight, maintainable, and scalable. A service based on REST is called a RESTful service.
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and Representational State Transfer (REST) are two answers to the same question: how to access Web services.
- A web service is any piece of software that makes itself available over the internet and uses a standardized XML messaging system. XML is used to encode all communications to a web service. For example, a client invokes a web service by sending an XML message, then waits for a corresponding XML response.
- Separate the client from the server.
- not hold state between request.
- use http and http methods.
console.log(xhr.statusTest)
8.what the four verbs?
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- DELETE
9.Anatomy of request ?
- The Request line
- The Header
- The Body
Getting started
For the purpose of this tutorial, I’ll work you through creating a RESTful API. To achieve this, we will create a RESTful todo list API (i.e. endpoints that will create a task, get or read list of all tasks, read a particular task, delete a task, and update a task).Assumptions
I presume that you already have your environment set up (i.e Node.js and MongoDB is installed).Kindly run
npm -v and mongo --version as these will show you the version of NPM and MongoDB installed on your machine.If you don’t have it installed, kindly go through this link on how to install it in order for us to create a server in Node and Mongodb.
If you do have Node and MongoDB installed, let's begin the tutorial with the following basic steps.
Open your terminal and kindly follow the following steps
Create a Folder name todoListApi -
mkdir todoListApicd todoListApinpm initPackage.json is a file that gives the necessary information to npm which allows it to identify the project as well as handle the project's dependencies.
npm init will prompt you to enter some information such as the app name, description, version, author, keyword and also ask if what you see is what you like.
You should have something like this eventually.
Kindly type yes and press enter to complete the creation of our package.json. Having done all these, your folder structure should look like this:
Create a file called server.js -
touch server.js.In this server, we will writing the protocols to create our server.
Create a folder called api -
mkdir apiInside this folder called api, create three separate folders called models, routes, and controllers by running
mkdir api/controllers api/models api/routes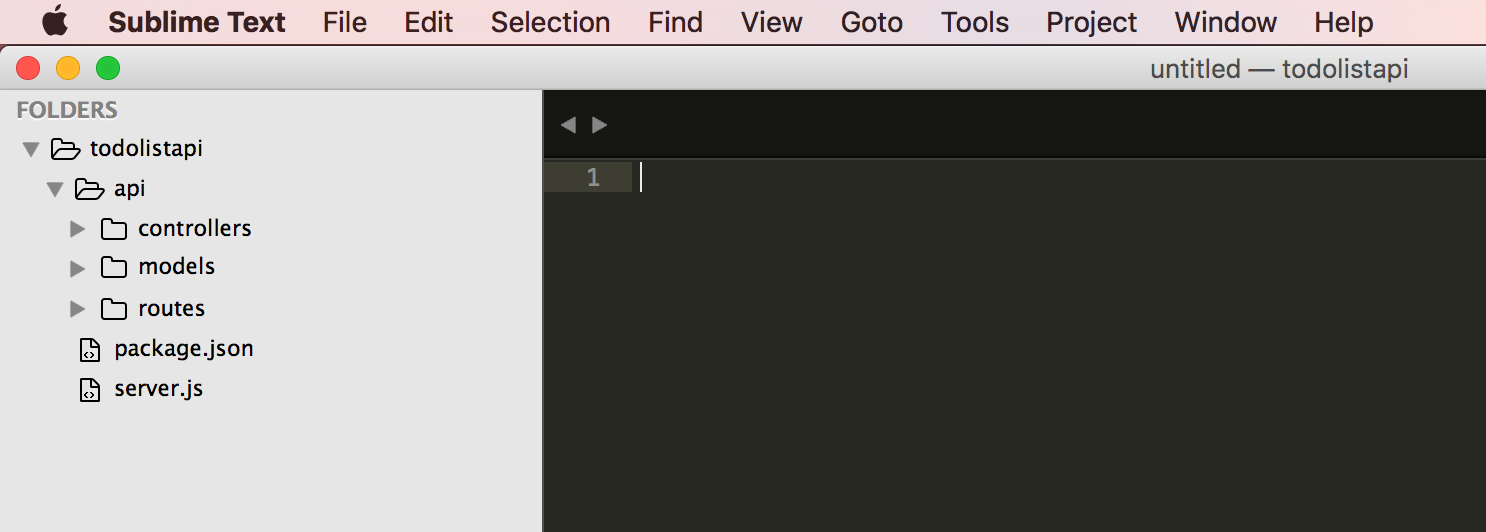
Create todoListController.js in the api/controller folder, todoListRoutes.js in the routes folder, and todoListModel in the model folder -
touch api/controllers/todoListController.js api/models/todoListModel.js api/routes/todoListRoutes.js Our folder structure should look like this now:Server setup
Let's install express and nodmon, express will be used to create the server while nodmon will help us to keep track of changes to our application by watching changed files and automatically restart the server.
➞npm install --save-dev nodemon➞npm install express --save
Open the package.json file and add this task to the scrip
var express = require('express'), app = express(), port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(port);console.log('todo list RESTful API server started on: ' + port);
app.listen(port);console.log('todo list RESTful API server started on: ' + port);
Setting up the schema
- First of all, let’s install mongoose - npm install mongoose --save
Why Mongoose?
Mongoose is what we will use to interact with a MongoDB(Database) instance.After installation, open the todoListModel.js file in your api/models folder and type the following code into the file and save.
'use strict';
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var TaskSchema = new Schema({
name: {
type: String,
Required: 'Kindly enter the name of the task'
},
Created_date: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now
},
status: {
type: [{
type: String,
enum: ['pending', 'ongoing', 'completed']
}],
default: ['pending']
}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('Tasks', TaskSchema);
From the code above, we required the mongoose in our file and then, we create a model of how our collection should look like.As you can see, it the task collection(table) will contain a name: a string, and the date it was created. It also contains task status which we have defined as pending - a default value for every task created.
Setting up the routes
Routing refers to determining how an application responds to a client request for a specific endpoint, which is a URI (or path) and a specific HTTP request method (GET, POST, and so on).Each of our routes has different route handler functions, which are executed when the route is matched.
Below we have defined two basic routes(‘/tasks’, and ‘/tasks/taskId’) with different methods
‘/tasks’ has to methods(‘GET’ and ‘POST’), while ‘/tasks/taskId’ has GET, PUT and DELETE.
As you can see, we required the controller so each of the routes methods can call it’s respective handler function.
module.exports = function(app) {
var todoList = require('../controllers/todoListController');
// todoList Routes
app.route('/tasks')
.get(todoList.list_all_tasks)
.post(todoList.create_a_task);
app.route('/tasks/:taskId')
.get(todoList.read_a_task)
.put(todoList.update_a_task)
.delete(todoList.delete_a_task);
};
Setting up the controller
Open todoListController.js file with your text editor( Sublime, Atom e.t.c) and let’s deep dive into coding.
In this controller, we would be writing five(5) different functions namely: list_all_tasks, create_a_task, read_a_task, update_a_task, delete_a_task. We will exported each of the functions for us to use in our routes.
Each of these functions uses different mongoose methods such as find, findById, findOneAndUpdate, save and remove.
res.send(err);
res.json(task);
});
};
exports.delete_a_task = function(req, res) {
Task.remove({
_id: req.params.taskId
}, function(err, task) {
if (err)
res.send(err);
res.json({ message: 'Task successfully deleted' });
});
};
Putting everything together
Connect our database by adding a url to the mongoose instance connection
Load the created model - task
Install bodyParser and use
bodyParser Parse incoming request bodies in a middleware before your handlers, available under the req.body property.
It exposes various factories to create middlewares. All middlewares will populate the req.bodyproperty with the parsed body, or an empty object ({}) if there was no body to parse (or an error was returned).
bodyParser Parse incoming request bodies in a middleware before your handlers, available under the req.body property.
It exposes various factories to create middlewares. All middlewares will populate the req.bodyproperty with the parsed body, or an empty object ({}) if there was no body to parse (or an error was returned).
Register our created routes in the server
var express = require('express'),
app = express(),
port = process.env.PORT || 3000,
mongoose = require('mongoose'),
Task = require('./api/models/todoListModel'),
bodyParser = require('body-parser');
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise;
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/Tododb');
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(bodyParser.json());
var routes = require('./api/routes/todoListRoutes');
routes(app);
app.listen(port);
console.log('todo list RESTful API server started on: ' + port);
Start MongoDB Server
Open your terminal and run mongod
rs on your nodemon running terminal. ⟹Testing via Postman
Now that everything is now connected, let’s test each of the routes and the respective methods.Open your postman and type:
http://localhost:3000/tasks in the enter request URL section and press enter.
On enter, you should see “[]” because there is nothing in the database yet.
On the same address, change the method to POST, click body and select “x-www-form-urlencoded”.
Then, enter name as the key and the corresponding task name as value.
After this, click on send button.
This should give you a response 200 ok
Then, enter name as the key and the corresponding task name as value.
After this, click on send button.
This should give you a response 200 ok
Adding a middleware
Having done all these, what happens if we entered a wrong route? say you entered 'http://localhost:3000/task', It responds with a message “Cannot GET /task”. Let’s add express middleware which could be used to return more interactive messages.Middlewares basically intercepts incoming http request and as such you can use them to perform several operations ranging from authentication to validations etc.
app.use(function(req, res) {
res.status(404).send({url: req.originalUrl + ' not found'})});